Ensuring secure communications remains crucial. Robocalls and call spoofing present significant challenges. These fraudulent activities not only cause inconvenience but also lead to significant financial losses and erosion of trust in telecommunication systems. The STIR/SHAKEN attestation framework addresses these issues by authenticating and verifying caller identities. According to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), millions of Americans fall victim to phone scams each year, resulting in billions of dollars in losses. Therefore, implementing robust security measures is essential to protect consumers and businesses alike.
Traditional methods of combating these issues, such as blacklists and basic caller ID. Additionally, they have proven inadequate in addressing the evolving tactics of fraudsters. Attackers use various techniques to disguise their identity and trick victims into divulging sensitive information. Undoubtedly, this impacts individual users and damages organizations’ reputations, potentially leading to legal consequences.
ANI validation further strengthens security by verifying the caller’s phone number. ANI provides the recipient with the caller’s phone number. Therefore, it allows the system to cross check this information against the provided caller ID. Moreover, this additional layer of verification ensures that the displayed number is accurate and not manipulated by fraudsters.
Integrating STIR/SHAKEN attestation with ANI validation significantly enhances security and trust in telecommunications. These technologies reduce the incidence of fraudulent activities by preventing caller ID spoofing and verifying the authenticity of calls. Certainly, this protects consumers from scams and helps businesses maintain their reputation and customer trust. This article explores the workings, benefits, and challenges of implementing a STIR SHAKEN solution with ANI validation.
Understanding STIR SHAKEN Solution
STIR/SHAKEN (Secure Telephone Identity Revisited/Signature-based Handling of Asserted Information Using toKENs) and Automatic Number Identification (ANI) validation offer robust solutions to these challenges. These technologies attach a digital certificate to the caller’s information, which the recipient’s carrier verifies. Additionally, this ensures the call originates from a legitimate source, preventing caller ID spoofing and enhancing telecommunication network security for any communication solution such as a wholesale VoIP Softswitch.
Types of STIR/SHAKEN Attestations
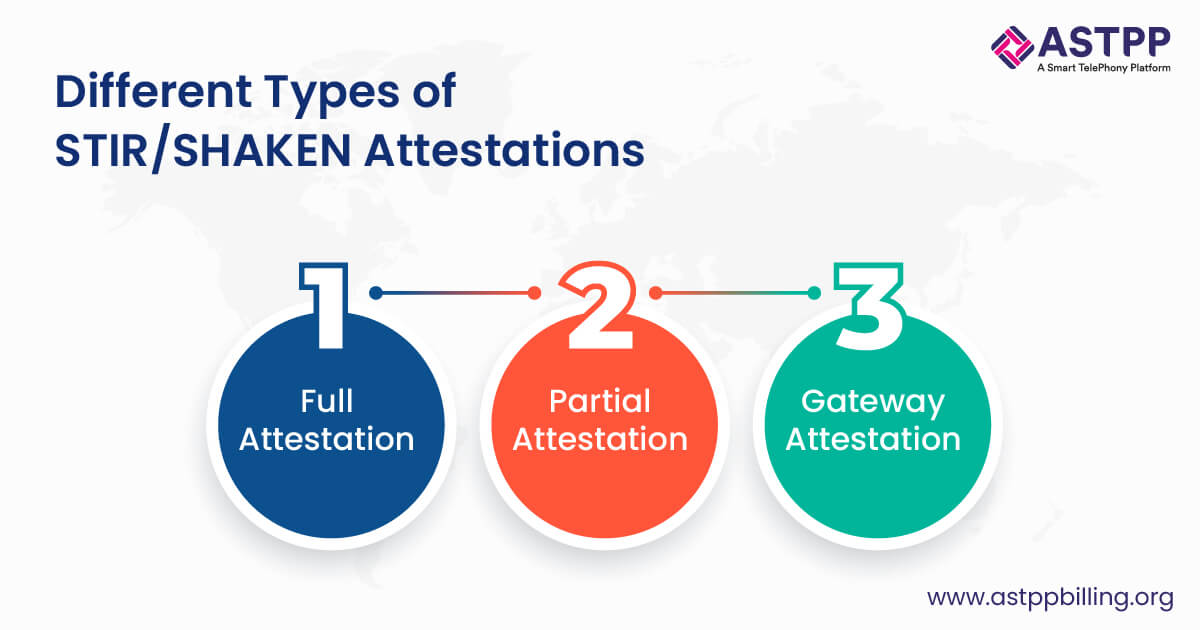
It provides different levels of assurance regarding the authenticity of the caller’s identity. Moreover, these attestations indicate the service provider’s confidence level in the caller’s identity and authorization to use the number being presented.
There are three main types of attestations:
Full Attestation (A)
Full Attestation (A) indicates the highest level of confidence in the caller’s identity. The originating service provider confirms that:
- The caller is authorized to use the calling number.
- The caller’s identity has been verified.
- The call originates from the service provider’s own network.
Typically, this type of STIR SHAKEN solution is used when the service provider has a direct relationship with the caller and can fully verify their identity. For instance, when a customer makes a call using their mobile phone directly connected to their telecom provider, the provider can confidently attest to the legitimacy of the call. Furthermore, full attestation ensures the highest level of security and trust in the call’s origin.
Partial Attestation (B)
Partial Attestation (B) indicates a moderate level of confidence in the caller’s identity. The service provider can attest that:
- The call originates from within its network.
- The caller’s identity can be partially verified.
Elevate Your Communication Security with STIR/SHAKEN Attestation and ANI Validation.
However, the service provider cannot confirm if the caller is authorized to use the calling number. Typically, this situation arises when the call originates from a business with multiple extensions, where the provider can verify the business but not the specific extension. Certainly, partial STIR/SHAKEN attestation provides some level of assurance. However, it is not as much as full attestation. It is useful in scenarios where calls pass through intermediate networks before reaching the recipient.
Gateway Attestation (C)
Gateway Attestation (C) indicates the lowest level of confidence in the caller’s identity. The service provider can only confirm that:
- The call was received from an international gateway or another network.
The provider has no direct knowledge of the call’s origin or the caller’s authorization to use the number. Interestingly, this type of STIR SHAKEN solution is common for calls originating from outside the provider’s network, such as international calls. Certainly, gateway attestation helps route calls through multiple networks while still providing a minimal level of security by acknowledging the call’s entry point into the provider’s network.
ANI Validation in STIR/SHAKEN
Defining ANI
Simply put, Automatic Number Identification (ANI) is a feature used in telecommunications systems that provides the recipient with the caller’s phone number. Unlike standard caller ID, which can be easily spoofed, ANI offers a more reliable means of identifying the caller. Certainly, ANI transmits the calling party’s number directly from the originating switch to the receiving switch, bypassing any potential for manipulation. Moreover, this type of STIR/SHAKEN attestation is direct transmission making ANI a crucial component in ensuring the integrity of the caller information.
Importance of ANI Validation

ANI validation proves crucial for secure communications. It serves several vital purposes:
Verification of Caller Identity
Certainly, ANI validation verifies the caller’s number, ensuring the number displayed to the recipient is accurate and not spoofed. Additionally, this verification process helps in identifying legitimate callers and filtering out fraudulent calls.
Prevention of Fraudulent Activities
By ensuring that the caller’s number is accurately presented, ANI validation helps prevent various types of fraudulent activities. For example, caller ID spoofing, where scammers manipulate the caller ID to appear as a trusted number. In short, this prevention is essential for maintaining the integrity of communications and protecting users from scams.
Enhancing Trust and Reliability
Integrating ANI validation with the STIR SHAKEN solution significantly enhances the overall security of communication solutions. Certainly, it provides an additional layer of verification, ensuring that calls are trustworthy. Moreover, this integration helps build user trust and confidence in the telecommunications system, as users can be more certain of the authenticity of incoming calls.
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Many regulatory bodies mandate the use of technologies like STIR/SHAKEN and ANI validation to combat robocalls and call spoofing. Implementing ANI validation helps telecom providers comply with these regulations, avoiding potential fines and ensuring they meet legal standards.
We recommend you read our blog covering all the details about STIR/SHAKEN and caller ID spoofing. It covers the complete insight on how to use STIR/SHAKEN to combat caller ID spoofing along with further insights on what it is.
Support for Enhanced Services
Undoubtedly, accurate ANI data is essential for advanced call routing and handling services, such as automatic call distribution (ACD) systems and customer relationship management (CRM) integrations. Moreover, these systems rely on accurate caller information to provide personalized and efficient service.
Improved Call Analytics
ANI validation provides accurate data that can be used for call analytics and reporting. This data helps organizations understand call patterns, identify potential fraud, and improve overall service quality.
How Does STIR/SHAKEN Work?

STIR/SHAKEN attestation attaches a digital certificate to caller information. This certificate includes details about the caller’s identity and the originating service provider. The service provider uses its private key to sign this information, creating an encrypted token that travels with the call.
The recipient’s carrier verifies this digital signature using the originating provider’s public key, accessible through a secure certificate repository. By decrypting the signature, the recipient’s carrier ensures the call originates from a legitimate source and that the caller ID remains untampered.
If verification succeeds, the carrier validates the caller ID and displays it to the end user with a high degree of trust. If verification fails, the call may be flagged as potentially fraudulent. This process effectively prevents fraudulent calls and enhances the security of telecommunication networks, providing a robust STIR SHAKEN solution.
Integrating STIR/SHAKEN open source components into this process ensures adaptability and continuous improvement from a global developer community, further strengthening the security framework.
Importance of Different Attestation Levels
Different levels of STIR/SHAKEN attestation play a crucial role in enhancing call security and trust. They allow service providers to convey varying levels of confidence in the caller’s identity, helping recipients make informed decisions about answering the call. By understanding the type of attestation associated with a call, carriers can implement appropriate measures, such as blocking or flagging potentially fraudulent calls.
Impact on Call Handling and User Experience
Higher attestation levels (Full and Partial) generally result in better user experiences by reducing the likelihood of fraudulent calls. They enable service providers to deliver calls with a higher degree of trust, enhancing overall customer satisfaction. Gateway attestation, while less secure, still provides valuable information about the call’s entry point, which can be used to improve call handling and fraud detection mechanisms.
Integration with STIR/SHAKEN open source Solutions
Integrating different attestation levels with STIR/SHAKEN open source solutions allow for continuous improvement and adaptability. Open-source implementations benefit from community contributions, ensuring that the latest security enhancements and best practices are incorporated, providing a robust and up-to-date security framework for telecommunications.
By leveraging the full, partial, and gateway attestations, the STIR SHAKEN solution ensures comprehensive protection against caller ID spoofing and enhances the integrity of communication networks.
Implementation of STIR/SHAKEN with ANI Validation
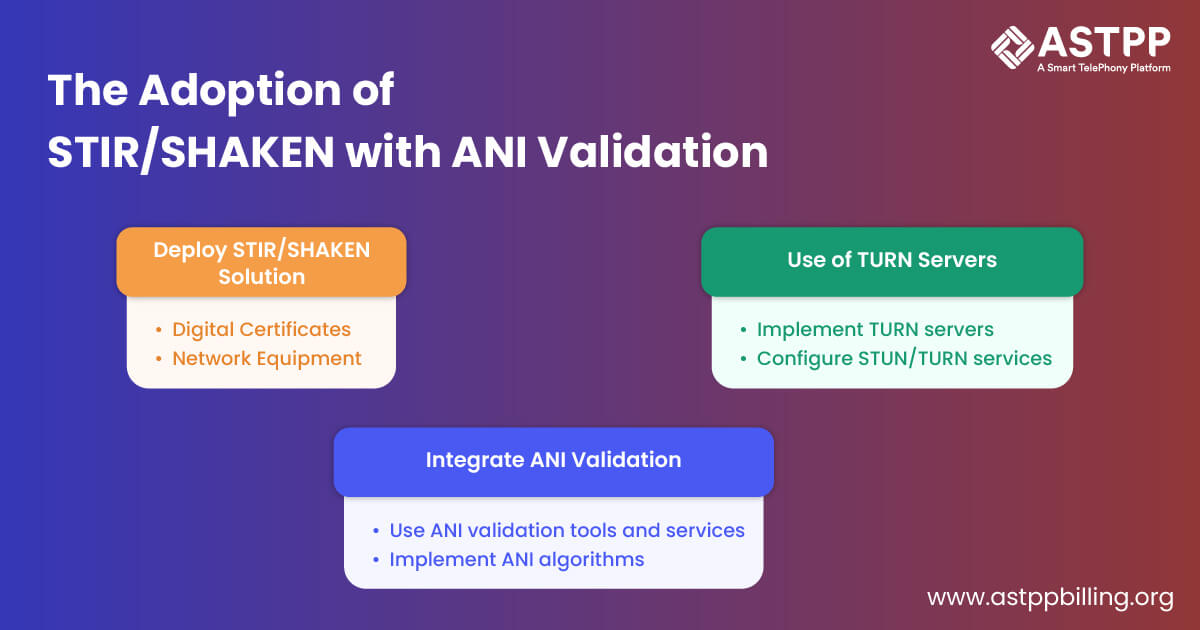
Begin by ensuring that your telecommunications network adheres to the STIR/SHAKEN attestation standards. This involves setting up the necessary infrastructure to handle digital certificates and integrating the cryptographic processes required for call authentication.
Steps for Integration
1. Deploy STIR/SHAKEN Solution
Procure digital certificates: Obtain the necessary digital certificates from trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). These certificates are crucial for signing and verifying the authenticity of calls.
Update network equipment: Ensure that all network equipment, such as switches and gateways, is compatible with STIR/SHAKEN protocols. This may require firmware updates or replacing outdated hardware.
2. Integrate ANI Validation
Use tools and services that validate ANI: Incorporate ANI validation tools that verify the caller’s number. These tools cross-check the ANI data against the displayed caller ID to ensure accuracy and prevent spoofing.
Implement ANI validation algorithms: Develop and deploy algorithms that automatically validate ANI data during the call setup process. These algorithms should be capable of identifying discrepancies and flagging potential fraud.
3. Use of TURN Servers
Implement TURN servers for NAT traversal issues: TURN (Traversal Using Relays around NAT) servers are essential for handling Network Address Translation (NAT) traversal issues, which can block direct peer-to-peer communication. TURN servers relay traffic when direct communication paths are unavailable, ensuring seamless call connectivity.
Configure STUN/TURN services: Set up and configure STUN (Session Traversal Utilities for NAT) and TURN services to work in conjunction with the STIR/SHAKEN solution. This setup helps in discovering public IP addresses and relaying traffic when necessary.
Technical Requirements and Challenges
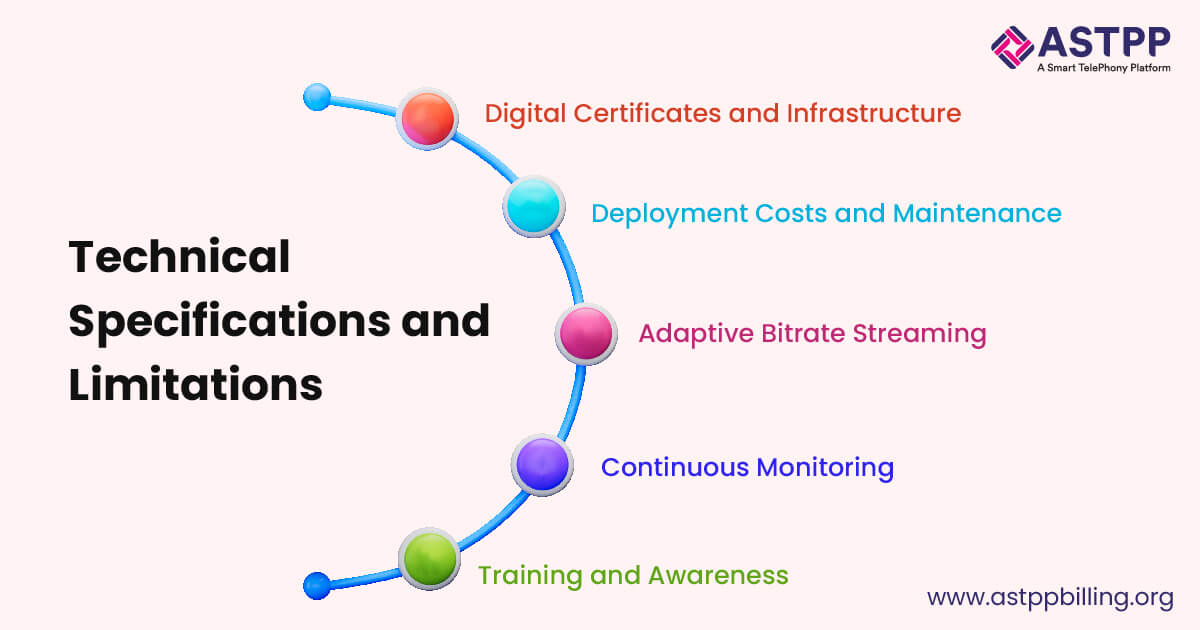
Digital Certificates and Infrastructure
Digital certificates: Implementation requires obtaining and managing digital certificates. These certificates are used to sign and verify call data, ensuring its authenticity.
Infrastructure upgrades: Integrating STIR/SHAKEN attestation and ANI validation often necessitates upgrading existing network infrastructure. This includes updating software and hardware to support the new protocols.
Deployment Costs and Maintenance
Initial deployment costs: The initial setup can be expensive, involving costs for acquiring digital certificates, upgrading infrastructure, and integrating validation tools.
Ongoing maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to keep the system effective. This includes renewing digital certificates, updating validation algorithms, and monitoring the network for compliance and performance.
Best Practices
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Use adaptive bitrate streaming: Adaptive bitrate streaming dynamically adjusts the video quality based on network conditions. Implementing this practice ensures that calls maintain high quality even when network conditions fluctuate.
Optimize media streams: Continuously optimize media streams to balance quality and bandwidth usage, providing the best possible user experience.
Continuous Monitoring
Implement monitoring tools like WebRTC Internals in Chrome: Use robust monitoring tools to track the performance of STIR SHAKEN solution and ANI validation systems. Tools like WebRTC Internals provide detailed insights into call quality and network performance.
Real-time analytics: Deploy real-time analytics to identify issues promptly and make necessary adjustments. Continuous monitoring helps maintain system integrity and performance.
Training and Awareness
Train technical staff: Ensure that your technical staff is well-trained in STIR/SHAKEN and ANI validation protocols. This training includes understanding how to deploy, manage, and troubleshoot these systems.
Raise awareness among users: Educate users about the benefits of STIR/SHAKEN and ANI validation. Inform them about how these
Concluding Notes
In conclusion, integrating STIR/SHAKEN attestation with ANI validation proves crucial for secure telecommunications. Understanding attestations, implementing the right technologies, and addressing challenges proactively enhance communication security. STIR/SHAKEN open source or custom solutions reduce fraud and improve customer trust. Embrace these technologies to build a secure communication infrastructure.





